前言
最近一直在刷算法题,感觉还是需要把基础打牢一点,就暂停了刷题,从基本的算法书开始看。
《小灰的算法之旅》一个很基础的书
二叉树
什么是二叉树?官方是这样定义的:在计算机科学中,二叉树是每个结点最多有两个子树的树结构。通常子树被称作“左子树”(left subtree)和“右子树”(right subtree)。
其实这些都是很基础的东西,之前数据结构也都学过了。所以一些东西就省去不表。。。
二叉树的数据结构
public class TreeNode {
public int data;
public TreeNode leftChild;
public TreeNode rightChild;
public TreeNode(int data){
this.data = data;
}
}
前序遍历生成二叉树
我采用的是递归的方式,这样最容易明白
//创建二叉树
//inputList 存放前序遍历的二叉树的list
public static TreeNode createBinaryTree(LinkedList<Integer> inputList){
TreeNode treeNode = null;
if(inputList==null||inputList.isEmpty()){
return null;
}
Integer data = inputList.removeFirst();
if(data!=null){
treeNode = new TreeNode(data);
treeNode.leftChild = createBinaryTree(inputList);
treeNode.rightChild = createBinaryTree(inputList);
}
return treeNode;
}
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> inputList = new LinkedList<Integer>();
inputList.add(3);
inputList.add(2);
inputList.add(9);
inputList.add(null);
inputList.add(null);
inputList.add(10);
inputList.add(null);
inputList.add(null);
inputList.add(8);
inputList.add(null);
inputList.add(4);
TreeNode head = createBinaryTree(inputList);
}
前序遍历二叉树
递归的写法
//前序遍历--递归的方式
public static void qian(TreeNode head){
if(head==null){
return;
}
System.out.println(head.data);
qian(head.leftChild);
qian(head.rightChild);
}
非递归的写法
//前序遍历--非递归的方式
public static void qian2(TreeNode head){
// 用栈来存放
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
while(head!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){
//迭代访问节点的左节点,并入栈
while(head!=null){
System.out.println(head.data);
stack.push(head);
head = head.leftChild;
}
//若节点没有左孩子,栈中弹出栈顶结点,访问节点右节点
if(!stack.isEmpty()){
head = stack.pop();
head = head.rightChild;
}
}
}
层次遍历
大致思路:
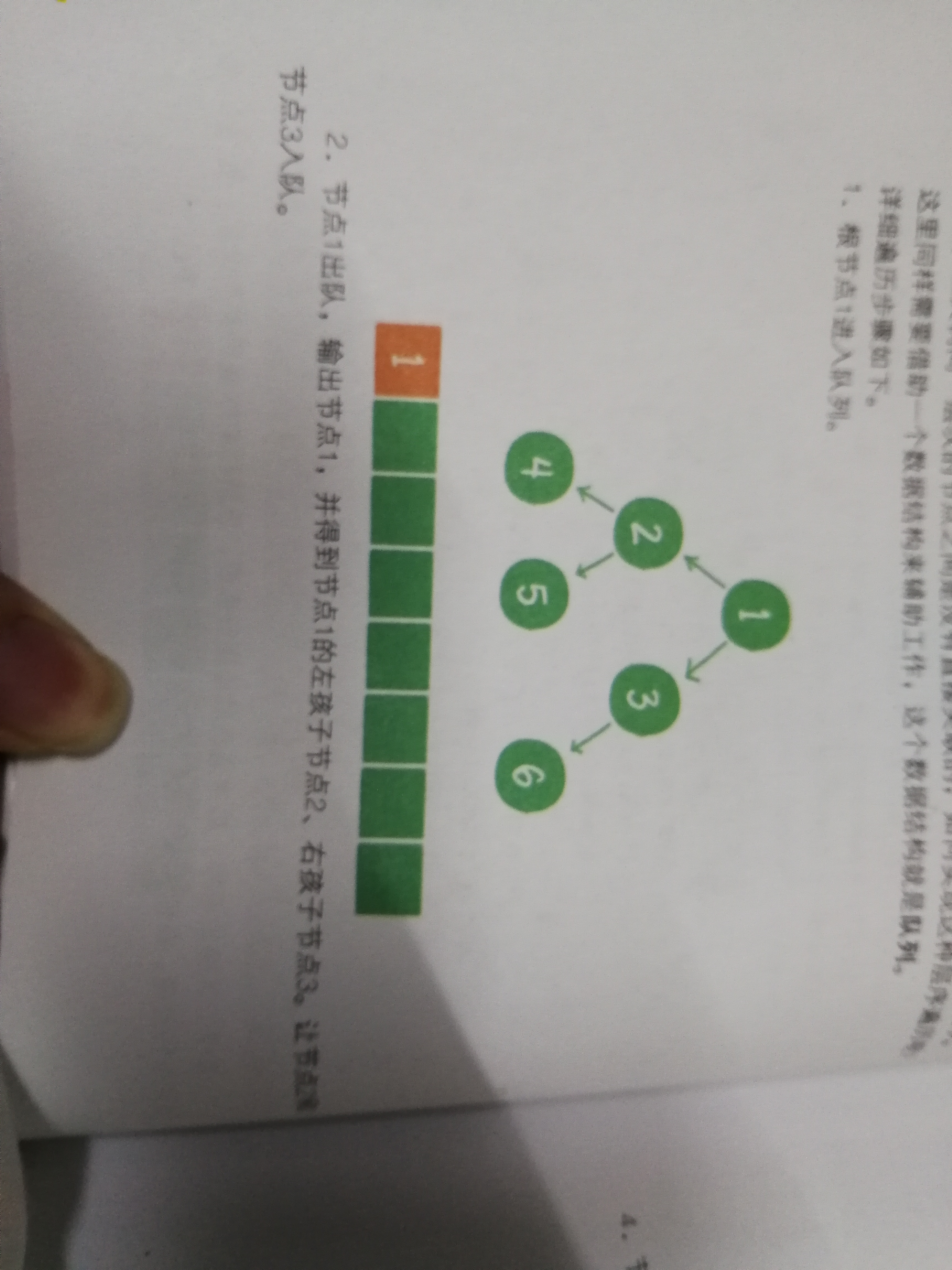
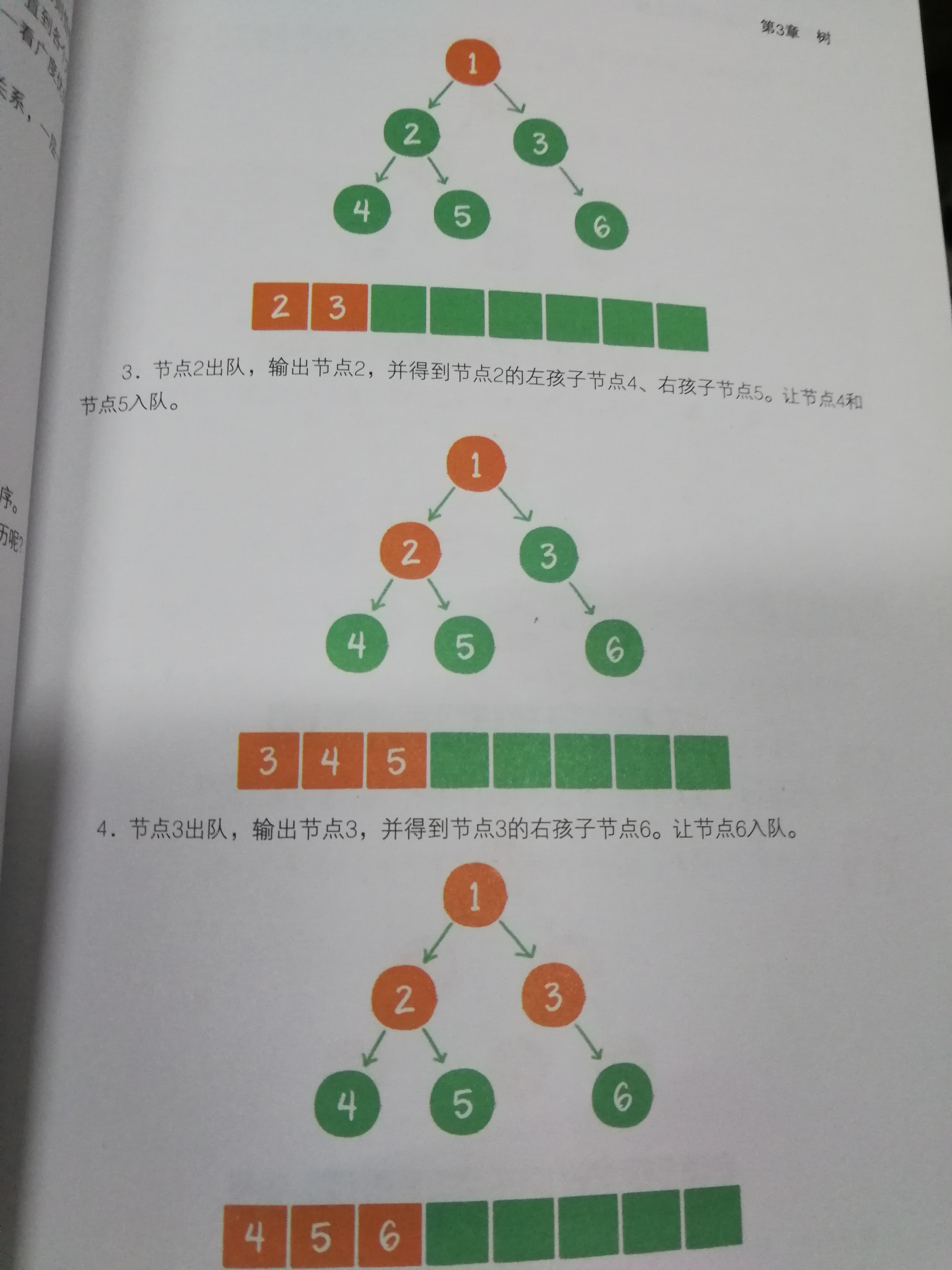
//广度优先遍历--层次遍历
public static void level(TreeNode head){
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(head);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode treeNode =queue.poll();
System.out.println(treeNode.data);
if(treeNode.leftChild!=null){
queue.offer(treeNode.leftChild);
}
if(treeNode.rightChild!=null){
queue.offer(treeNode.rightChild);
}
}
}